
It also helps when assigning responsibility to individuals and assists in motivating employees and other staff to achieve the organization’s performance targets. Hidden causes of under-performance that are not identified can represent a risk. Or maybe there are some areas where you’re thriving with over-performance and making significant savings. Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications.
Why Is Standard Deviation Often Used More Than Variance?
These are just a few examples, and the specific causes of unfavorable variances will vary depending on your industry and unique circumstances. In simpler terms, it means everything went exactly according to plan, with no surprises (either positive or negative) in terms of costs, revenues, or other financial metrics. This occurs when the actual results perfectly match the budgeted or planned figures.
Example of Overhead Variance
- The labor rate variance is determined by calculating how much you spent on labor hours and seeing how that number compares to your original budget.
- If the actual rate that you pay to your workforce is higher than a standard rate that you would pay for the same amount of work, then the rate variance will be unfavorable.
- Here, variance analysis becomes the vital tool that enables you to quickly identify such changes and adjust your strategies accordingly to manage your financial performance and optimize cash forecasting.
- Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
Variance analysis helps management to rely on the principle of management by exception. Depending on your goals, you can analyze any of the following variances to optimize your operational performance. For companies that have manufacture it is important to keep track of the production quantities and prices. At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site.
What Is Variance in Statistics? Definition, Formula, and Example
Excel is tremendously flexible and capable of producing insightful variance analysis — as long as your data is structured and reliable. Many finance professionals regrettably spend hours each day aggregating and processing their data. The inefficiencies compound as your data sets grow larger and your ERP doesn’t offer the reporting structure necessary for analysis. Finally, there’s material price variance, which is the actual unit cost of an item minus its standard cost. If the standard cost was $10, you have a favorable efficiency variance because you paid less than the standard.
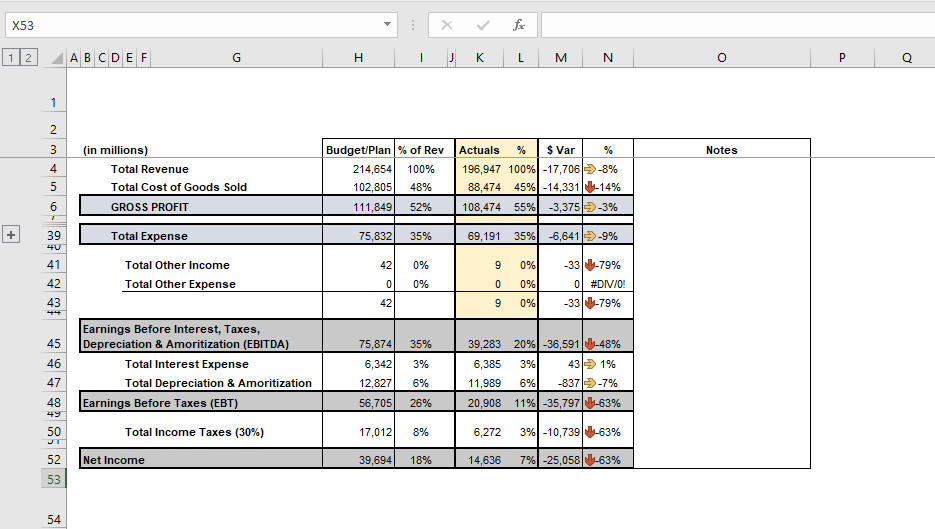
In such cases, the management will only examine more cost areas where differences exceed these limitations. This is a prime example of how variance analysis is used to achieve efficiency. Variance analysis helps to identify cost differences between actual performance and desired performance.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
This approach allows for a more detailed understanding of cost variances beyond simply comparing actuals to the budget. This variance can be further broken down into price variance (difference between actual and budgeted price per unit) and quantity variance (difference between actual and budgeted quantity used). This cycle helps us unravel the reasons behind the differences between what we expected to happen financially (budgeted or planned figures) and what actually happened (our real-world results). If you are an accounting, finance or data science professional, you might be familiar with the term ANOVA.
While financial variance analyses can give you a deeper level of understanding of your business’ finances, it’s essential to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of this reporting tool before going all in. On the other hand, a fixed overhead variance occurs when there is a difference between the standard fixed overhead for actual output and the actual fixed overhead. Rate variance shows the difference in actual and standard price rate for the actual hours of work.
While unfavorable variances, meaning actual results falling short of expectations, are generally unwelcome surprises, they’re not always a bad thing. It’s simply the difference between what you expected (budgeted) and what actually happened. It’s like the gap between your planned destination and the actual road you end up taking. However, vehicle title, tax, insurance and registration costs by state for 2021 for a deeper analysis, we need to consider different types of variances, leading to more specific formulas. When these stakeholders determine strategies for their business unit, it is your analysis and recommendations fueling those decisions. This is why the accuracy, and quality of your data are imperative for insightful analysis.
By analyzing this variance, you can figure out what went wrong and take steps to improve your sales performance in the next quarter. Here, variance analysis becomes the vital tool that enables you to quickly identify such changes and adjust your strategies accordingly to manage your financial performance and optimize cash forecasting. Budget variance analysis are important to understand the reasons behind the deviations from the budgeted amounts. It enables the identification of avenues for enhancing business processes, boosting revenue, and cutting costs. By examining revenue variances, you can uncover possibilities for long-term efficiency improvements and increased business value. It’s a broader approach that doesn’t necessarily consider standard costs and can be used for various expense categories, including materials, labor, and overheads.
For example, if a contractor who makes a dress for you charges $20 per hour, but you budgeted $22 per hour, you would have a favorable variance. Let’s say a mechanic anticipated $10,000 in profits for one month but generated $8,000, that would be a $2,000 unfavorable variance. Suppose it’s determined through a variance analysis that the fluctuation in anticipated profits can be traced to rising costs of automobile parts. In that case, the mechanic can adjust their standard prices to make up for variable costs or find a cheaper vendor. For example, if the actual cost is lower than the standard cost for raw materials, assuming the same volume of materials, it would lead to a favorable price variance (i.e., cost savings).
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year. Labour Variance occurs when the actual labor cost differs from the projected labor Cost. In comparison, Mix is due to using a combination of two materials in a different proportion during the production process. Both purchasing and production costs depend on each other, so we have to look into not only the purchasing cost but also the Production Cost to know the total variance.
